Veolia’s solutions in support of the ecological transformation of car manufacturing
The electric vehicles are an integral part of the environmental protection measures and the achievement of zero CO2 emission transport. Today the electric vehicles become increasingly popular and more affordable thanks to the new technologies, which address more and more successfully a number of challenges related to mileage and access to charging stations.
At the same time, the demand for electric cars on the old continent is increasing, stimulated by the measures taken by governments. Thus, for example, only last year’s sales have reached a record 2.59 million (based on data of the consultancy company JATO Dynamics). On an annual basis, the volume increases by 15%, and compared to 2020 – by 92%.
The transition to the electric vehicles is accelerated and inevitable but at the same time, it is also challenged. A few main question marks remain over the short life cycle of lithium-ion batteries, and over the past few years – over the difficulties faced in relation to the lithium supply.
The increased quantities of lithium-ion batteries, the rapidly changing provisions, and the growing concerns for decarbonization of the activities lead to the need to organize large-scale operations and create sustainable and effective business models.
In addition, the prices of the metals identified as strategic – lithium, cobalt and nickel, are essential for the production of electric batteries and therefore, they are crucial for the energy transition. However, the extraction and production of these metals are concentrated in several geographical areas, which is already a prerequisite for geopolitical tension in terms of resources and distribution channels in the context of a growing demand. In addition, the extraction and refining of these metals entail significant costs for people and environment.
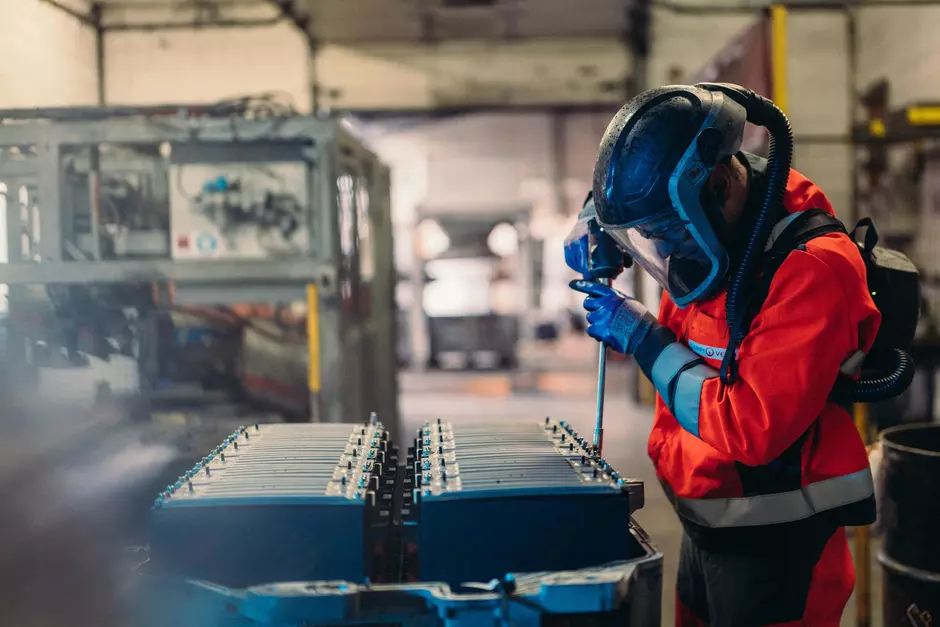

Actual recycling is important for several main reasons. The first one – exactly lithium-ion batteries are one of the main factors for the environmental footprint of electric vehicles. That footprint could be significantly reduced through recycling. The other important aspect of recycling is the resources for the batteries, which have been affected by the geopolitical turmoil of recent years. The expansion and imposing of recycling programs could reduce the heavy reliance on imports of the strategic metals lithium, nickel and cobalt, needed for battery production. It should not be underestimated the fact that batteries could pose a serious threat to the environment and people, as they contain chemicals and are highly flammable. The proper treatment and process management related to their recycling is of utmost importance.
The legislation on the management and processing of end-of-life batteries for electric vehicles is developing and changing rapidly in order to support the recycling operations and the use of recycled materials for manufacturing new batteries.
What solutions does Veolia offer?
Veolia has more than 50 years of experience in the management of hazardous waste and this is one of the fastest evolving businesses of the company, which has been recycling alkaline batteries for 11 years, and it is very logical for this expertise to serve as a good foundation for finding solutions also for the larger batteries from electric vehicles. At present, Veolia has several operating plants for battery recycling – two in Europe and one in China. The plant in North America is under construction.
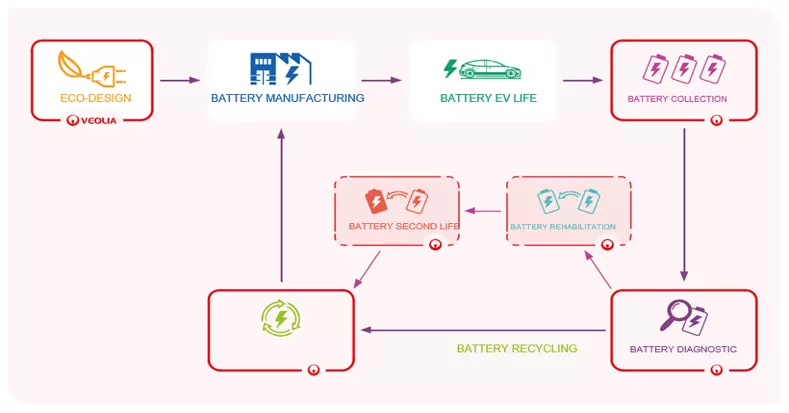
Currently, the focus of the company is the creation of an eco-design of EV batteries to facilitate their reuse and recycling, figuratively speaking – batteries would get a "second life".
Such "rebirth" of end-of-life batteries has already become a fact through combining the processes in a closed loop, starting from the collection of EoL batteries to dismantling, extraction and purification of the metals – and by improving existing mechanical and other battery recycling processes. The metals are extracted by means of a chemical hydrometallurgical process. After that, they are converted into recycled materials. This serves to address several serious challenges and develops the strategic raw materials’ recycling value chain, because if to date the main constituents of batteries have been imported, "tomorrow" they can be regenerated within Europe.
Recycling activities include two types of battery waste – scrap from current battery production processes and end-of-life batteries. Veolia establishes with its partners a closed-loop battery recycling model in compliance with the provisions and manages to develop safe and local raw materials supply. Also, the recycling process is already considered a secure and sustainable source of supply of strategic metals for batteries such as cobalt, nickel and lithium.
It is extremely important for the recycling process to comply with the highest quality and safety standards and not only give a new life to waste, but it is also a step towards circular economy.
At the international conference Automotive and Battery Forum 2023, held in Sofia at the end of April 2023, Mariana Iteva, Deputy Country Director of Veolia for Bulgaria, said: "The transition to electrical vehicles is the chance for the automotive industry to address carbon emissions. However, a few major problems have been identified – the short life cycle of lithium-ion batteries and the difficulties faced in relation to the raw materials supply," added Iteva during the forum.
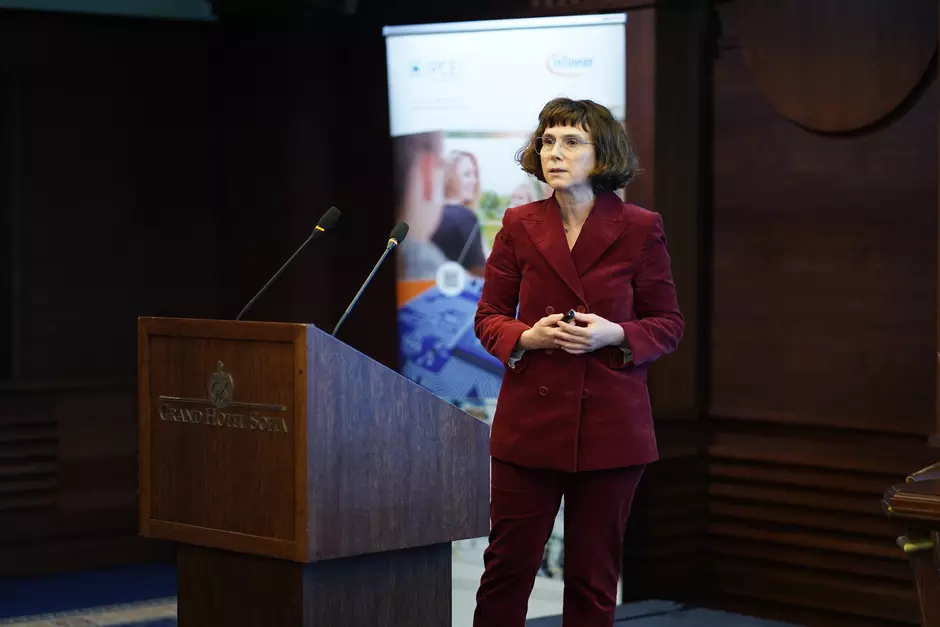

"Our company has established a closed battery recycling loop with full recovery of the extracted precious metals such as lithium, cobalt, nickel, and copper. We expect 3 to 7 million tons of batteries from e-vehicles to be recycled in Europe by 2030, and currently only Veolia Group recycles around 30,000 tons of batteries a year," stated Mariana Iteva at the forum.
She emphasized that the biggest source of greenhouse gas emission regarding the EVs is no longer the operation, but the production – the materials for the lithium-ion batteries, as well as their assembly phase are key factors for the environmental footprint during the production of an electric vehicle, and recycling is a step towards circular economy and the addressing of this major problem.


